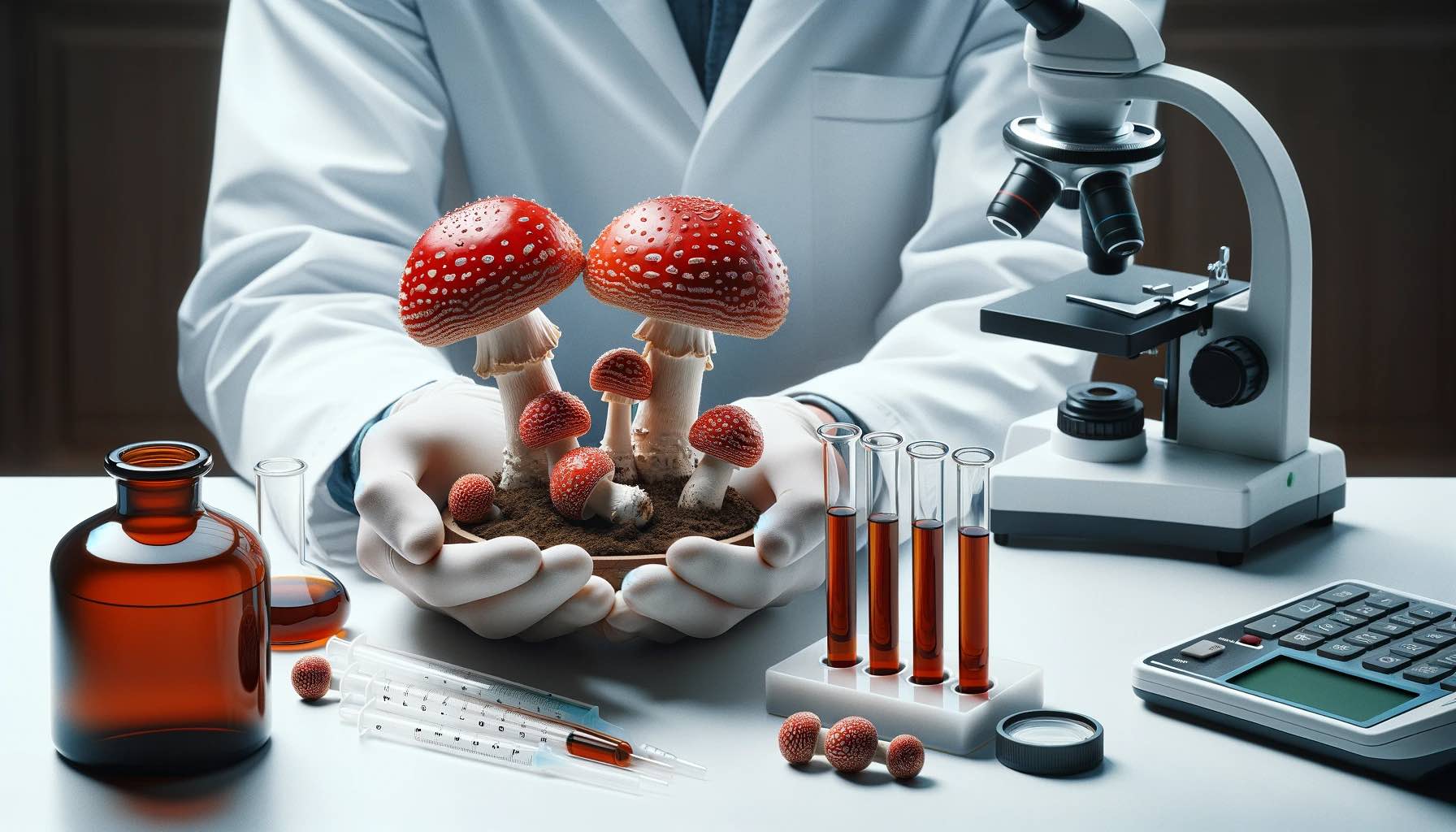
Agaric mushrooms have been used for centuries. However, its transition into modern supplement form, particularly gummies, requires careful consideration of safety and efficacy. Unlike many other mushroom species used in supplements, Amanita Muscaria contains toxic compounds if not properly prepared. This inherent risk underscores the critical need for thorough and independent testing throughout the production process.
Third-party testing refers to the analysis of products by an independent laboratory without affiliation with the manufacturer or seller. These labs employ consistent scientific protocols to assess different facets of the product, including its chemical makeup and any potential contaminants. For Amanita Muscaria gummies, this testing is essential to verify safety, potency, and overall quality.
Key areas of focus in third-party testing
- Compound identification and quantification – The primary focus is on identifying and measuring muscimol, the main psychoactive compound in Amanita Muscaria. Equally critical is detecting and quantifying ibotenic acid, a precursor to muscimol that is neurotoxic at high doses. Proper mushroom preparation should convert most ibotenic acid to muscimol, and third-party testing can confirm that this conversion has occurred adequately.
- Contaminant screening – This involves testing for potential contaminants such as heavy metals, pesticides, microbial growth, and mycotoxins. Given that mushrooms absorb substances from their environment, ensuring consumer safety is crucial for consumer safety.
- Consistency and potency – Third-party labs verify that each batch of gummies contains a consistent amount of active compounds. This is essential for consumers who rely on precise dosing for their desired effects.
- Allergen testing – As gummies involve various ingredients beyond just mushroom extract, testing for common allergens is a crucial safety measure.
- Shelf-life studies – Independent laboratories can conduct stability testing to determine the product’s shelf life and ensure that the active compounds remain stable over time.
Process of third-party testing
The testing process typically begins with sample collection, where representatives from an independent laboratory collect samples directly from the production facility or retail products. Subsequently, these samples are subjected to thorough analysis using sophisticated scientific instruments like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry, and gas chromatography. For Amanita Muscaria gummies, special attention is given to the extraction and analysis of muscimol and ibotenic acid. The testing protocols must be carefully designed to accurately measure these compounds within the complex matrix of a gummy product.
Benefits of third-party testing
The implementation of rigorous third-party testing in the production of these mushroom-based gummies offers numerous benefits:
- Consumer Safety – By verifying the absence of toxins and confirming proper preparation, third-party testing ensures that the final product is safe for consumption.
- Quality Assurance – Regular testing helps maintain consistent quality across different batches and over time.
- Transparency – Manufacturers who engage in third-party testing and openly share the results demonstrate a commitment to transparency, which builds consumer trust.
- Regulatory compliance – As regulations around mushroom-based supplements evolve, third-party testing can help manufacturers stay compliant with emerging standards.
- Product improvement – Independent labs can offer insights that help manufacturers refine production processes and improve products.
Role of consumers
While manufacturers bear primary responsibility for product quality and safety, consumers also play a role. By demanding transparency and seeking out products with rigorous third-party testing, consumers can drive the industry towards higher standards. When considering amanita mushroom gummies, consumers should look for products that provide clear information about third-party testing practices. This may include batch-specific test results or certificates of analysis from reputable laboratories.